41 questions and answers
For a broadcast super heterodyne AM receiver having no RF amplifier, the loaded quality factor Q of the antenna coupling circuit is 100. Now if the intermediate frequency is 455 KHz, then determine the image frequency and its rejection ratio at an incoming frequency of 1 MHz.
Given that quality factor Q = 100 The intermediate frequency fi = 455KHz
Write short notes on:
The second method of the non-coherent AM detection is Envelope Detector. In this circuit modulated signal Vin(t) is used as an input signal. The source resistance RS is connected in series with the active non-linear p-n junction diode.
Compare PAM, PWM and PPM
PAM, PWM and PPM stands for Pulse Amplitude Modulation, Pulse Width Modulation and Pulse Position Modulation. In the PAM system carrier signal is rectangular pulse and that is why this system is called PAM.
An AM transmitter has an un-modulated carrier power of 10 kW. It can be modulated by a sinusoidal modulating voltage to a maximum depth of 40%, without overload. If the maximum modulation index is reduced to 30%, what is the extent up to which the modulated carrier power can be increased without overloading?
Given that Pc = 10kW Modulation index µ = 0.4
Find the Fourier transform of the following:
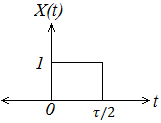
Fig. 1
From the figure, we have the function x(t) = 1 for 0 < t ≤ τ/2 and otherwise x(t) = 0
Draw the block diagram of a super heterodyne receiver. Explain the function of each block. Explain the significance of the name super hetero dyne. How RF sections suppress the image channel? Why is up – conversion used in super heterodyne receive? Define image Rejection Ratio.
Super heterodyne receivers was proposed as an alternative to TRF receiver which suffers from selectivity problem .The basic super heterodyne receiver is most widely used receivers at present. Super heterodyne principal is also used in television and radar receiver. In the super heterodyne receivers, the received RF signal voltage is combined with the local oscillator voltage and is converted into a signal of lower fixed frequency.
"FM and PM are different but inseparable." – Justify the statement.
The expression for FM and PM are almost identical. FM and PM cannot be distinguished at a constant modulating frequency.
What are Narrowband FM and Wideband FM?
A narrow band FM is the FM wave with a small bandwidth. The modulation index β of narrow band FM is small as compared to one radian. Hence, the spectrum of narrowband FM consists of the carrier and upper side band and lower side band.
Explain with proper expression
The modulation index in AM wave is defined as the ratio between amplitude of the modulating signal and amplitude of the carrier signal. The mathematical representation is given below
The maximum deviation allowed in an FM broadcast system is 75 kHz. If the modulating signal is a single tone sinusoid of 10 kHz, find the bandwidth of the FM signal. What will be the change in the bandwidth, if the modulating frequency is double? Determine the bandwidth when modulating signal amplitude is also double.
Given that ∆f=75KHz and fm=10KHz According to the Carson’s thumb rule the bandwidth BW=2(∆f+fm )=2(75+10)=170KHz
Copyright © 2025 MindStudy
A product by Shunya Intelliware Solution
(Registered under MSME Uddyam)
