The higher-level entity type (or super-class) has the attributes that are common to all of its lower-level entity types (or sub-classes). These common attributes of the super-class are inherited by all of its sub-classes. This property is known as attribute inheritance.
The ER Model has the power of expressing database entities in a conceptual hierarchical manner. As the hierarchy goes up, it generalizes the view of entities, and as we go deep in the hierarchy, it gives us the detail of every entity included.
Going up in this structure is called generalization, where entities are clubbed together to represent a more generalized view. For example, a particular student named Mira can be generalized along with all the students. The entity shall be a student, and further, the student is a person. The reverse is called specialization where a person is a student, and that student is Mira.
Generalization
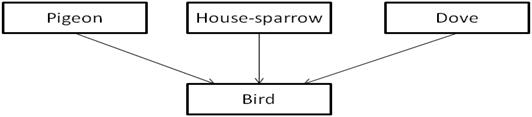
As mentioned above, the process of generalizing entities, where the generalized entities contain the properties of all the generalized entities, is called generalization. In generalization, a number of entities are brought together into one generalized entity based on their similar characteristics. For example, pigeon, house sparrow, crow and dove can all be generalized as Birds.
Specialization
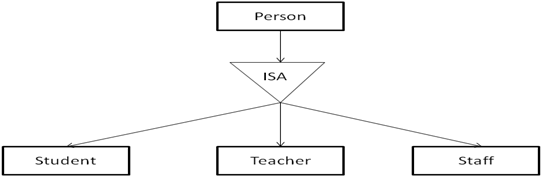
Specialization is the opposite of generalization. In specialization, a group of entities is divided into sub-groups based on their characteristics. Take a group ‘Person’ for example. A person has name, date of birth, gender, etc. These properties are common in all persons, human beings. But in a company, persons can be identified as employee, employer, customer, or vendor, based on what role they play in the company.
Similarly, in a school database, persons can be specialized as teacher, student, or a staff, based on what role they play in school as entities.