Generally, Computer animation is a visual digital display technology that processes the moving images on screen. In simple words, it can be put or defined as the art or power of giving life, energy and emotions etc. to any non-living or inanimate object via computers. It can be presented in form of any video or movie. Computer animation has the ability to make any dead image alive. The key/main concept behind computer animation is to play the defined images at a faster rate to fool the viewer so that the viewer should interpret those images as a continuous motion of images.
Computer Animation is a sub-part or say small part of computer graphics and animation. Nowadays, animation can be seen in many area around us. It is used in a lot of movies, films and games, education, e-commerce, computer art, training etc. It is a big part of entertainment area as most of the sets and background is all build up through VFX and animation.
History of Computer Animation:
| YEAR | DEVELOPMENTS |
|---|---|
| 1906 | “Humorous phase of funny faces” – 1st animated movie/film. |
| 1909 | “Gertie the trained Dinosaur” – Cartoon was developed. |
| 1913 | Felix the cat” and “Old doc Yak” – Cartoon series was developed. |
| 1923 | Cartoon movie Alice’s Wonderland was created. |
| 1926 | “Prince Achmed” – 1st full length animated movie. |
| 1928 | “Mickey Mouse” – First cartoon with sound (developed by Walt Disney). |
| 1970 | “Scanimate” – 1st analog video synthesizer. |
| 1977 | “Star War” – First popular movie using animation. |
| 1993 | “Jurassic Park”, movie using VFX and animation. |
| 1995 | “Disney Pixar’s Toy Story” – 1st computer animation featuring film. |
| 2003 | Movies like: “The Matrix Reloaded” and “The Matrix Revolutions”, used virtual cinematography. |
| 2006 | Video Game named “Play Station 3” was developed. |
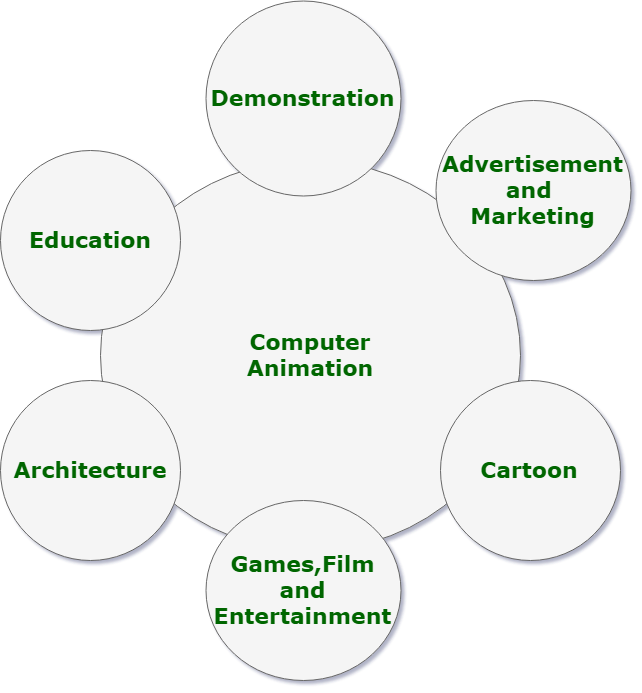
Applications of Computer Animation:
Methods/Techniques:
- Frame by Frame (Traditional Method):
Earlier, in traditional method, animation was done by hands because of the absence of the computer-aided drawing facilities. And, these traditional method required a lot of effort for even making a short video because of the fact that every second of animation requires 24 frames to process.
- Procedural:
In Procedural method, set of rules are used to animate the objects. Animator defines or specify the initial rules and procedure to process and later runs simulations.Many of the times rules or procedure are based on real world.s physical rule which are shown by mathematical equations.
- Behavioral:
According to this method/technique, to a certain extent the character or object specifies/determines it’s own actions which helps / allows the character to improve later, and in turn, it frees the animator in determining each and every details of the character’s motion.
- Key Framing:
A key frame in computer animation is a frame where we define changes in an animation. According to key framing, a storyboard requirement is must as the animator/artist draws the major frames (frames in which major/important changes can be made later) of animation from it. In key framing, character’s or object’s key position are the must and need to be defined by the animator, because the missing frames are filled in those key position via computer automatically.
- Motion Capture:
This method of animation uses the live action/motion footage of a living human character which is recorded to the computer via video cameras and markers and later, that action or motion is used/applied to animate the character which gives the real feel to the viewers as if the real human character has been animated. Motion Capture is quite famous among the animators because of the fact that the human action or motion can be captured with relative ease.
- Dynamics:
In this method, simulations are used in order to produce a quite different sequence while maintaining the physical reality. Physics’s laws are used in simulations to create the motion of pictures/characters. High level of interactivity can be achieved in this method, via the use of real-time simulations, where a real person performs the action or motions of a simulated character.
