Several modes of electromagnetic waves, corresponding to the solution of the Maxwell’s equations, propagate inside a waveguide. A given waveguide has a definite cut-off frequency for each allowed mode. When a wave is incident with a frequency greater than the cut-off frequency for a given mode, it propagates through the waveguide for that particular mode without any attenuation. In all other cases, the wave will be attenuated after a very short distance of travel within the guide.
Cut – off frequency depends on the outside dimensions of the aperture. Increasing the aperture size decreases fc and decreasing the aperture size increases fc.
In general, a good design target is to plan for 10-15 dB of shielding effectiveness with fc at a minimum of third harmonic of the highest fundamental frequency of concern. For example, if the highest operational frequency of concern in a system is 1 GHz, a good waveguide design should provide 10-15 DB of EMI attenuation up to at least 3 GHz. Note that current regulations specify that EMI measurements must be taken up to the fifth harmonic of the highest frequency. Depending on your system, the design target may need to be adjusted.
The cut-off frequency fc for TE mode of rectangular wave guide is
\[ f_c = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{\mu\varepsilon}} \sqrt{\frac{m^2}{a^2} + \frac{n^2}{b^2}} \]
The cut-off frequency fc for TM mode of rectangular wave guide is
\[ f_c = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{\mu\varepsilon}} \sqrt{\frac{m^2}{a^2} + \frac{n^2}{b^2}} \]
The cutoff frequency for TE10 mode is
\( f_{c}=\frac{c}{2a} GHz \), where \( c=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu\epsilon}}=3\times 10^{8} m/s \) and unites of parameters ‘a’ and ‘b’ are in meter.
The cutoff frequency for TE01 mode is
\( f_{c}=\frac{c}{a} GHz \), where dimensions a=2b and \( c=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu\epsilon}}=3\times 10^{8} m/s \) unites of parameters ‘a’ and ‘b’ are in meter.
The cutoff frequency for TE11 mode is
\( f_c=\frac{c\sqrt{5}}{2a}GHz \), where dimensions a=2b, \( c=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu\epsilon}}=3\times 10^{8} m/s \)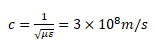 and unites of parameters ‘a’ and ‘b’ are in meter.
and unites of parameters ‘a’ and ‘b’ are in meter.
